Aspect
Ratio
Length
ratio between the width and length, or the ratio of the
longest side to the shortest side of a 2D element. For
example, a square has the same width and length and therefore
has an aspect ratio of 1. As a shape digresses from the
square shape, the aspect ratio becomes smaller. A value
closer to 1 is ideal. This ratio has significant effect
on the analysis result and if the value is very small,
it may be hard to obtain normal analysis results.
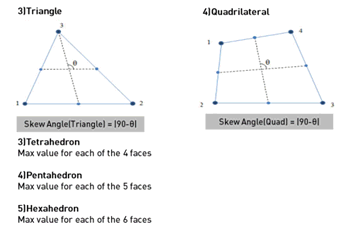
Skew Angle
How
much the shape digresses from the rectangular shape (90
degrees), measured in angles. A quadrilateral forms a
90 degree angle, the inclination angle is 0 degrees and
this value increases as the shape strays from the quadrilateral.
For a solid element, the inclination angle is checked
for each face and the smallest value is chosen as the
inclination angle. A value closer to 0 is better.
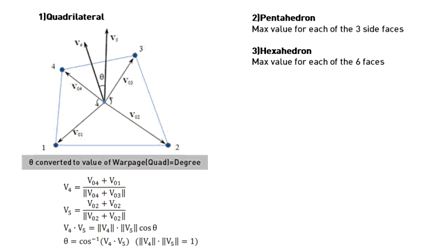
Warpage
Evaluates
how much the shape is out of the plane. For a quadrilateral
2D element with all nodes on the same plane, the value
is 0. The value increases as the shape strays from the
plane. For a solid element, the warpage is checked for
each rectangular face and the smallest value is chosen
as the warpage value. A value closer to 0 is better. This
item has significant effect on the analysis result and
if the value is very large, it may be hard to obtain normal
analysis results.
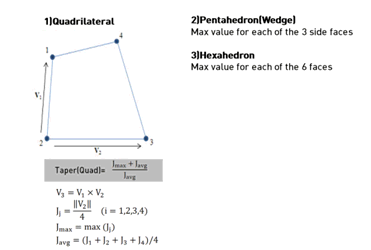
Taper
Geometrically
calculates how much the quadrilateral digresses. It is
not applied to triangular elements. A quadrilateral has
a value of 1, and the value decreases as it digresses
(becomes closer to a triangular shape) from its rectangular
shape. For a solid element, the taper value is checked
for each face and the smallest value is chosen as the
taper value. A value closer to 1 is better.
Jacobian
Ratio
The Jacobian determinant
is calculated at each Gauss integral point on the mesh
the Jacobian ratio is the ratio between the largest and
smallest Jacobian determinant value. For 2D elements,
the Jacobian determinant is calculated on the element
projected onto a plane. For solid elements, the Jacobian
determinant is calculated directly. If the quadrilateral
element is not convex, the negative value is outputted
and the analysis is not performed properly. A higher value
is better.
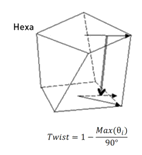
Twist(Solid)
Value that represents
the twist between 2 opposing faces in a solid.
Element length
Check
the edge length of an element. Here, the minimum and maximum
values can be set.
Mesh set
After
the quality check has finished, press ‘Send’ to define
a different mesh set. The user can specify the name of
the mesh set. |


